Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest . Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed under pressure. See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases.
from www.slideshare.net
Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility. Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed under pressure.
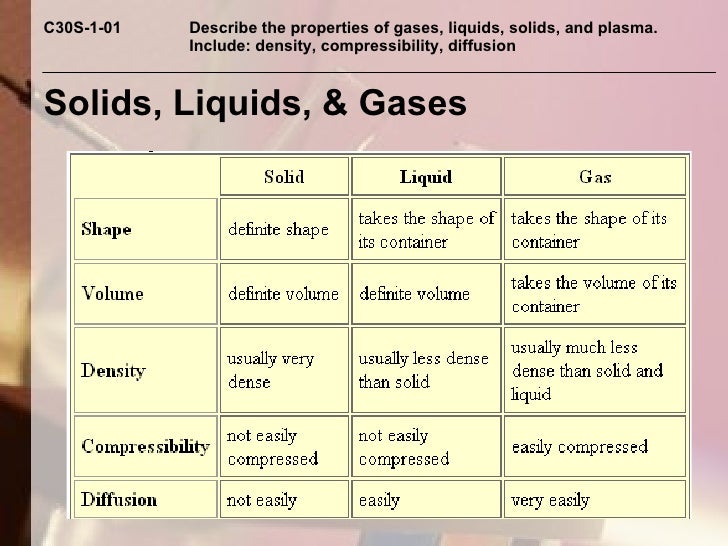
Unit 1 Notes
Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed under pressure. Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility.
From www.vecteezy.com
States of matter, Solid, liquid, gas varying particle arrangement and Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. The atoms in a solid or a. Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed under pressure. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility. A solid. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From narodnatribuna.info
Chemistry Works Inter Conversion Of Solid Liquid And Gas Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.youtube.com
Compressibility of solid, liquid and gas YouTube Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility. Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. Web learn how to use. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From igcsechemistryrevision.weebly.com
iGCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION HELP Particles & Equations Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From general.chemistrysteps.com
States of Matter Solid, Liquid, Gas, and Plasma Chemistry Steps Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From slideplayer.com
Unit 7 States of matter and the Behavior of Gases ppt download Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed under pressure. Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.pinterest.ph
Properties of Solids, Liquids, Gases Compared Teachoo Science Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility. Web compressibility is. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.youtube.com
Fluid properties Explained. YouTube Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.pinterest.com
States of Matter (solids, liquids and gases) The Chemistry Journey Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed under pressure. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. Web learn how the kinetic. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.learnatnoon.com
The Molecular Differences Between Solids, Liquid and Gases Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From mungfali.com
Solids Liquids Gases Chart Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. Web. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.slideshare.net
(Science) Matter Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. The atoms in a solid or a. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. Web compressibility. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From mungfali.com
Solids Liquids Gases Chart Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed under pressure. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. Web learn how to. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From psiberg.com
Properties of Solid, Liquid, Gases A Comparison Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes and strong attractive forces of the. The atoms in a solid or a.. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.yaclass.in
Compressibility of solids, liquids and gases — lesson. Science State Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. Web in thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the. A solid has a fixed shape, whereas. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.slideshare.net
Unit 1 Notes Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest A solid has a fixed shape, whereas fluids (liquid and gas) have no fixed shape. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility. Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From www.youtube.com
compressibility of solids, liquids and gases YouTube Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. Web learn how to define and calculate the isothermal compressibility and isobaric thermal expansivity of substances. Web learn the definition and examples of solids, liquids and gases, and how they differ in compressibility. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be applied to liquids, taking into account the nonzero volumes. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.
From allaboutchemistry123.blogspot.com
What are solid, liquid, and gases? All About Chemistry Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest Web compressibility is the measure of how much a given volume of matter decreases when placed under pressure. See the generalized compressibility chart, examples, and. The atoms in a solid or a. Web learn how to use the compressibility factor to correct the ideal gas law for real gases. Web learn how the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be. Compressibility Of Solid Liquid And Gases Highest To Lowest.